At the start of 2024, AMD revealed their new lineup of Ryzen 8000G processors, promising enhanced performance and efficiency for a variety of computing tasks, including gaming.

One of the most intriguing aspects of the Ryzen 8000G series, though, is its integrated graphics capability, which begs the question: just how capable are these processors when it comes to gaming without the need for a dedicated graphics card? This question is not only relevant for budget-conscious gamers but also for those seeking compact and power-efficient gaming setups.
From casual titles to graphically demanding AAA releases, let’s take a look at what you can expect from these integrated solutions.
The Ryzen 8000G Lineup
There are four new CPUs in this lineup, three available to buy individually and one limited to certain pre-built partner systems slated to be released by the end of Q1 2024.
Overall, this is what the lineup looks like:
- AMD Ryzen 7 8700G: 8 cores/16 threads, 5.1GHz turbo, Radeon 780M integrated graphics, Ryzen AI
- AMD Ryzen 5 8600G: 6 cores/12 threads, 5.0GHz turbo, Radeon 760M integrated graphics, Ryzen AI
- AMD Ryzen 5 8500G: 6 cores/12 threads, 5.0GHZ turbo, Radeon 740M integrated graphics
- AMD Ryzen 3 8400G: 4 cores/8 threads, 4.9GHz turbo, Radeon 740M integrated graphics (only available in specific pre-built systems)
As you can see, not all of the range comes fitted with AMD’s NPU technology, just the top two offerings in the stack. Both include AMD Ryzen AI, which AMD says is “uniquely able to accelerate AI software capabilities in your PC to optimize AI workloads, improve AI processing efficiencies, and unlock exciting experiences like AI-powered noise cancellation.”
All of the 8000 series processor models do feature AMD’s most powerful built-in graphics though, with the use of Radeon 700M technology, albeit at differing power levels for different price points. The top offering in the stack - the Ryzen 7 8700G - features Radeon 780M graphics which AMD says is “the fastest built-in graphics you can get in a desktop processor”.

The Gaming Power of the Ryzen 8000G Series
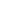
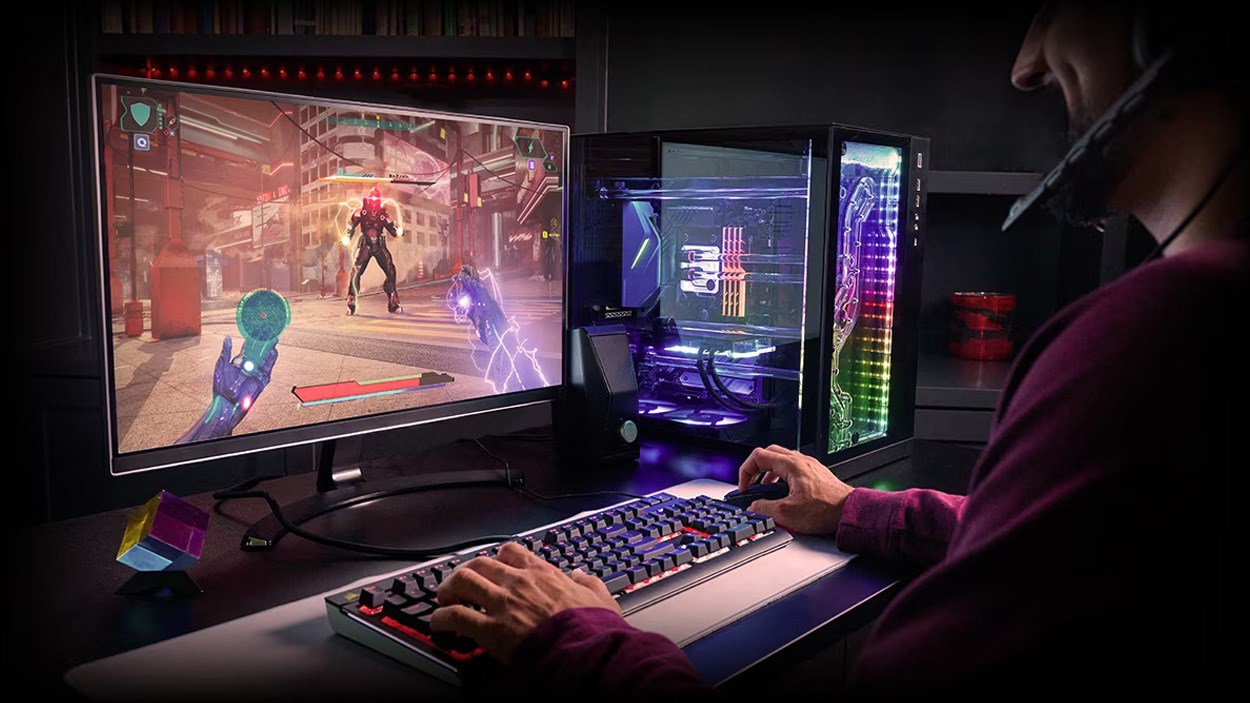
During their reveal presentation, AMD placed a lot of emphasis on the gaming power of this lineup, specifically in the top-of-the-stack option - the 8700G. They claimed via various benchmarks that it can smoothly play some seriously demanding games at 1080p, albeit with graphical settings on low.
As shown in this slide from their CES presentation, the Ryzen 8700G can play games like Cyberpunk 2077, Farcry 6 and Assassin’s Creed Valhalla all at around 60FPS and above. And in this day and age, 60FPS is typically the baseline goal so to achieve that without a dedicated graphics card is quite the achievement.
On the other end of the spectrum, in less graphically intensive games such as Esports titles like League of Legends and Dota 2, the 8700G can reach frame rates in the hundreds. This is ideal for players wanting a competitive edge and to not fall behind the enemy team.
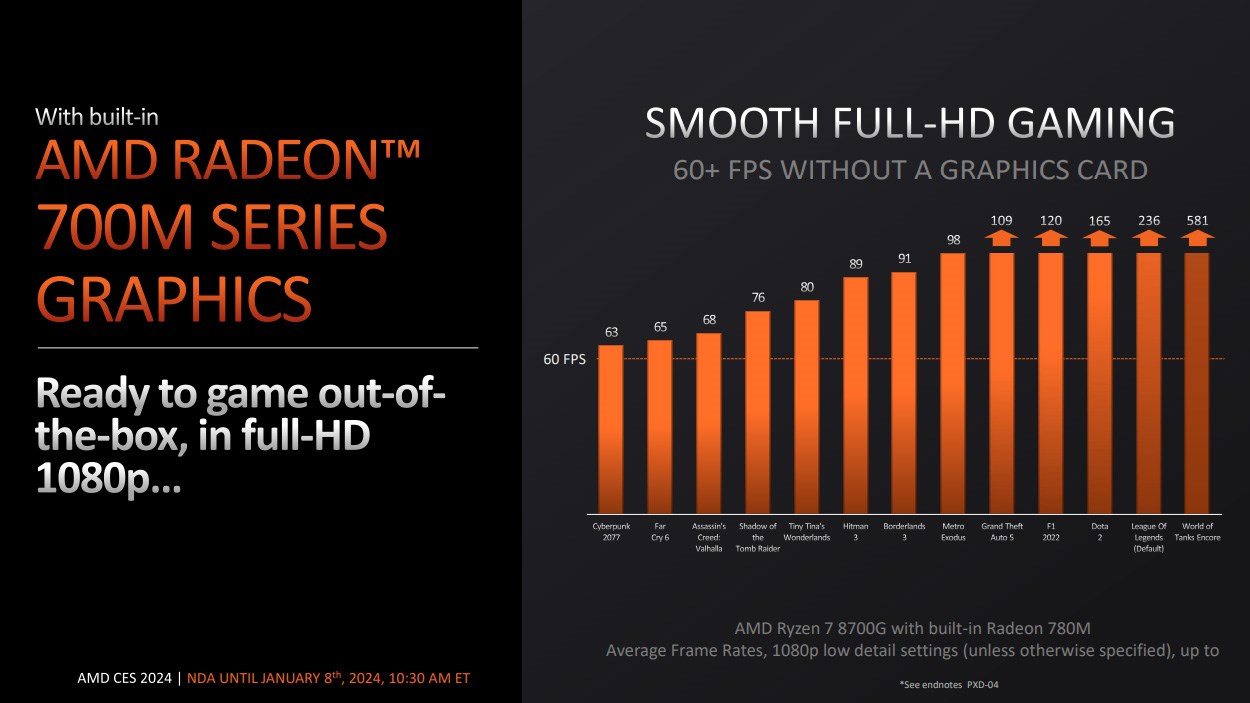
Arguably even more interestingly, AMD also did a test with the Ryzen 8700G against a system with a CPU and GPU combo - the Intel 13400F and an Nvidia GTX 1650. In Alan Wake 2, Starfield, and Star Wars Jedi: Survivor, the 8700G outperformed the Intel/Nvidia combo by up to 1.3x. And even though it couldn’t outperform the CPU & GPU combo in every title, it did still come close in the ones that fell behind.
Diving more into the middle-tier offerings in the lineup - the 8500G and 8600G - they have fewer cores and threads and smaller GPU chips, but according to other testers and reviewers, still manage to run a lot of games well.
The 8600G being the more powerful of the two obviously fares better, achieving a respectable 34 FPS playing Farcry 6 at 1080p in PCGamer’s benchmarks, this time with graphics set to high.
The 8500G chip, though, with its reduced power, is much better suited to those only looking to play competitive games at low settings where sacrificing visual quality for increased frames is the norm.
Overall though, it does seem that AMD has made tremendous advancements in integrated graphics, and each of the 3 main processors will get games up and running at a fairly enjoyable experience.
Benefits of gaming on integrated graphics
Gaming without a dedicated graphics card presents numerous benefits that cater to both casual and enthusiast gamers alike. Firstly, it offers a cost-effective solution, eliminating the need for an additional hardware purchase. This is particularly advantageous for budget-conscious gamers or those who are building a PC on a limited budget.
Moreover, gaming without a graphics card contributes to space-saving and portability, as it reduces the overall size and weight of the gaming setup. This is especially beneficial for gamers who prefer compact or portable setups, such as gaming laptops or mini-ITX systems. Additionally, by relying on integrated graphics solutions, gamers can enjoy lower power consumption, leading to reduced energy bills and a more environmentally friendly gaming experience.
Overall, gaming without a graphics card provides a convenient, efficient, and eco-conscious approach to enjoying a wide variety of gaming titles.
Limitations of gaming on integrated graphics
While offering convenience and cost-effectiveness, integrated graphics do also come with certain limitations that can impact gaming performance and visual quality. One significant limitation is the relatively lower performance compared to dedicated graphics cards.
Integrated graphics processors share system memory with the CPU, leading to reduced overall performance, especially in graphically demanding tasks. This can result in lower frame rates, reduced visual fidelity, and limitations in the resolution and graphical settings of games.
Additionally, integrated graphics may struggle with running the latest AAA titles at optimal settings, often requiring users to lower graphics settings or resolutions to achieve playable frame rates. Another limitation is the lack of dedicated video memory (VRAM), which can affect the smoothness and responsiveness of gameplay, particularly in games with large textures or complex scenes.
Furthermore, integrated graphics may face compatibility issues with certain games or software that require specific graphics features or hardware support. Overall, while integrated graphics offer a viable solution for basic gaming and everyday computing tasks, they may not provide the level of performance and visual quality demanded by hardcore gamers or enthusiasts.
Conclusion
If you are looking for a cheaper way into the world of PC gaming, an AMD 8000G series CPU will serve you well. The top two options will let you play demanding AAA titles smoothly if you don’t mind dialling back the visual settings a bit, and the lower power options in the range will provide a stellar experience in the Esports side of things where high frames matter more than lifelike graphics.
Ultimately, it looks like the 8000G series (or the 8700G at the very least) can play any game you throw at it with decent frame rates. You’ll just have to be content with turning the graphics down low.